In today’s digital landscape, data is one of the most valuable assets for any organization. Unexpected events—ranging from hardware failures and cyberattacks to natural disasters—can jeopardize critical information and disrupt operations. Building a resilient data backup and disaster recovery plan is essential to ensure business continuity, protect sensitive information, and minimize downtime. A well-structured plan enables organizations to quickly restore systems, maintain operational efficiency, and recover lost data with minimal financial and operational impact. By proactively addressing potential risks, businesses can safeguard their information infrastructure against both predictable and unforeseen challenges.
Implementing effective DR solutions is a crucial component of any comprehensive strategy. These solutions provide the tools and processes to efficiently replicate, store, and recover data, ensuring that even in the event of a disruption, vital information remains accessible. A resilient plan goes beyond simple backups, incorporating redundancy, regular testing, and clearly defined recovery protocols. With careful planning and the right combination of strategies, organizations can create a robust framework that maintains data integrity and supports long-term operational resilience.
The first step in planning is identifying which applications, databases, and infrastructure components are mission-critical. Conduct a comprehensive Business Impact Analysis (BIA) to understand which operations, data, and infrastructure your business can’t run without. The BIA should also identify potential threats—including ransomware, hardware failure, natural disasters, and human error—and evaluate their expected impact. This foundational process is crucial for prioritizing what needs the most rigorous protection and the fastest recovery, aligning resource allocation with business priorities.
Prioritizing starts with categorizing data and systems. Some data may require real-time protection, while archived financial records might only need weekly snapshots. By conducting a gap analysis, you’ll uncover which systems are currently protected, which are at risk, and where to focus resilience enhancements.
Once you understand what you need to protect, defining Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) becomes the next focus. RTO is the maximum acceptable duration your systems can be down following a disruption; RPO is the maximum age of files that must be recovered from backup storage for normal operations to resume. Precise metrics guide the technical and procedural design of your backup and disaster recovery plan, ensuring alignment with business tolerance for downtime and data loss.
Work closely with business stakeholders to accurately document RTOs (Recovery Time Objectives) and RPOs (Recovery Point Objectives) for each critical application or dataset. These benchmarks determine your backup frequency, the recovery infrastructure required, and the response speed required during an incident.
READ ALSO: Should I Use Lopulgunzer? A 5-Point Honest Breakdown
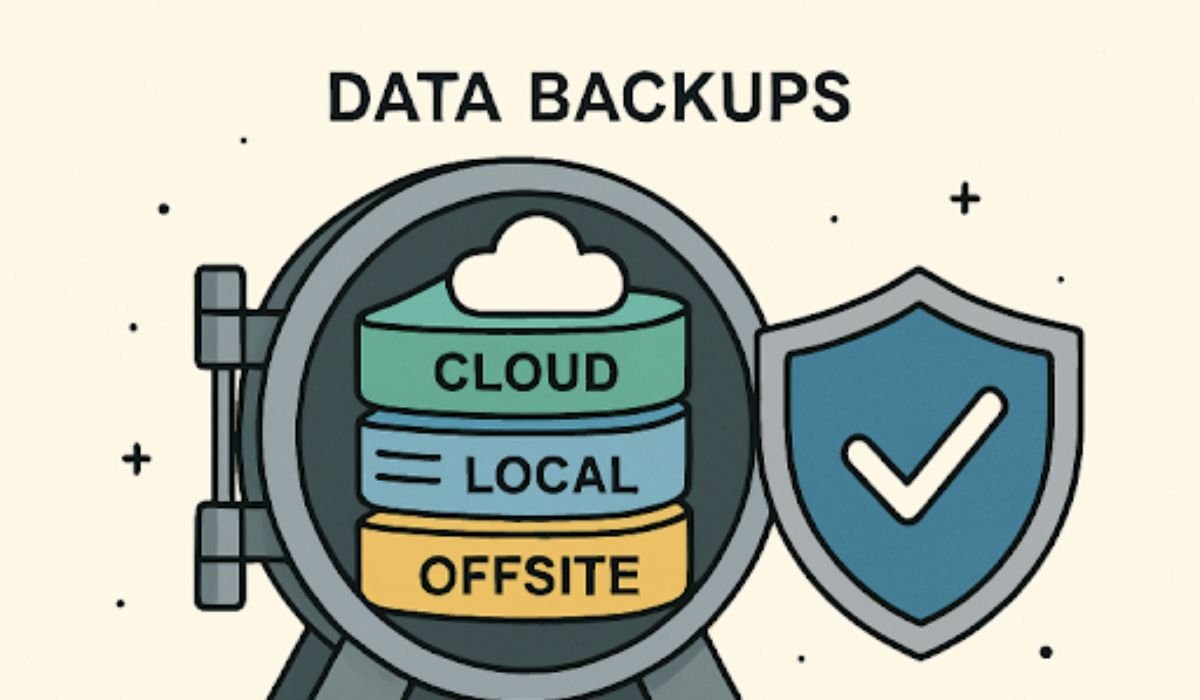
Modern backup strategies should go beyond simple file copies. The widely recommended 3-2-1 rule provides an effective benchmark: maintain three copies of your data (one primary and two backups), store them on two different media types, and keep one copy offsite. This approach protects data from a range of threats, including cyberattacks and physical disasters, by creating multiple independent recovery points.
The integrity of backups is paramount. Schedule regular incremental and full backups, and periodically perform manual validations by restoring data in test environments to ensure data integrity. This proactive approach will ensure your backups are truly recoverable when disaster strikes.
The cloud offers elasticity, rapid deployment, and cost-efficiency, making it a valuable tool for disaster recovery planning. Cloud-based solutions provide automated off-site backups, streamlined recovery workflows, and robust geographic redundancy. When evaluating potential cloud partners, examine their compliance certifications (such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2), security policies, and documented recovery SLAs.
The cloud can be a key enabler for DR for both small businesses and large enterprises, especially when integrated with on-premises infrastructure for hybrid resilience. Make sure any cloud provider you select aligns with your compliance needs and data locality requirements.
Automation minimizes human error and streamlines backup and restore processes, ensuring that essential data is consistently protected. Automate regular backups, data replication, and even the failover procedures necessary for disaster recovery. However, automation is not “set and forget.” Regularly test your recovery plan—at least quarterly—using realistic scenarios to ensure its effectiveness. Tabletop exercises and full-scale drills will reveal gaps, timing issues, or employee misunderstandings before a real emergency unfolds.
During a disaster, clarity and speed in communication are essential. Your plan should outline who will communicate, what information will be communicated, and through which channels. Predefine messages and roles, ensuring internal teams, business partners, and external stakeholders receive crucial information promptly and accurately. Lack of communication can fuel panic and disorder—clear direction ensures coordinated, effective response.
Even the best-documented plan will fail if your team isn’t prepared to execute it. Provide targeted training for all employees, particularly those in key roles within the disaster response chain. Assign disaster recovery responsibilities—such as backup management, system monitoring, or external communications—to specific roles, and use routine drills and simulations to keep skills sharp.
Cyber threats, compliance requirements, and business operations evolve, and so must your disaster recovery plan. Schedule annual reviews or trigger them after any major system or personnel change. Continuously monitor new risks, regulatory shifts, and IT developments to keep your plan aligned with current needs and best practices.
Building a resilient data backup and disaster recovery plan is essential for safeguarding critical business operations. By assessing business needs, defining clear recovery objectives, implementing layered backup strategies, and leveraging cloud solutions, organizations can minimize downtime and data loss. Automation, regular testing, staff training, and clear communication further strengthen the plan’s effectiveness. Continuous monitoring and updates ensure the plan evolves as emerging threats and organizational changes emerge. With these measures in place, businesses can maintain operational continuity, protect valuable data, and respond confidently to any unexpected disruption.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Sofware Doxfore5 Dying: The Essential Migration Guide